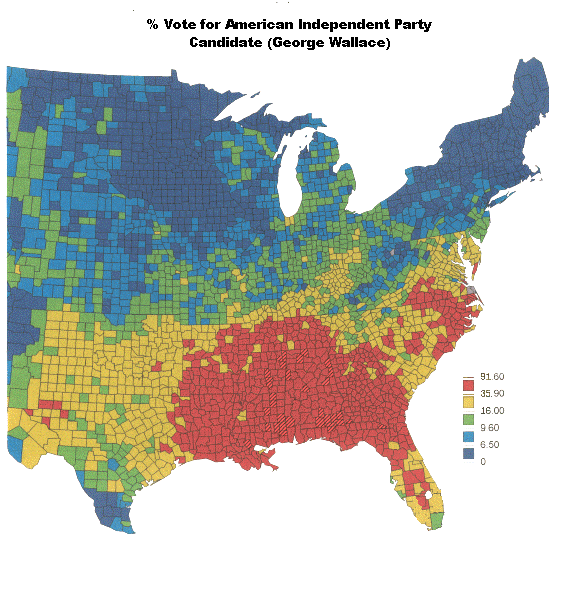
In 1968, George Wallace ran as a third-party candidate against Nixon and Humphrey, on an explicitly segregationist platform. Humphrey had been the main champion of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 in the Senate; Nixon, while no civil rights activist, rejected an overtly racist platform. Feeling abandoned by both parties, Southern white racists flocked to Wallace's cause, winning him the Deep South states of Ark., La., Miss., Ala. and Ga.
Political analyst and Nixon campaigner Kevin Phillips, analysing 1948-1968 voting trends, viewed these rebellious Southern voters as ripe for Republican picking. In The Emerging Republican Majority (Arlington House, 1969), he correctly predicted that the Republican party would shift its national base to the South by appealing to whites' disaffection with liberal democratic racial and welfare policies. President Nixon shrewdly played this "Southern strategy" by promoting affirmative action in employment, a "wedge" issue that later Republicans would exploit to split the Democratic coalition of white working class and black voters. (See John Skrentny, The Ironies of Affirmative Action (U Chicago Press, 1996)). This strategy soon produced the racial party alignments that prevail today.